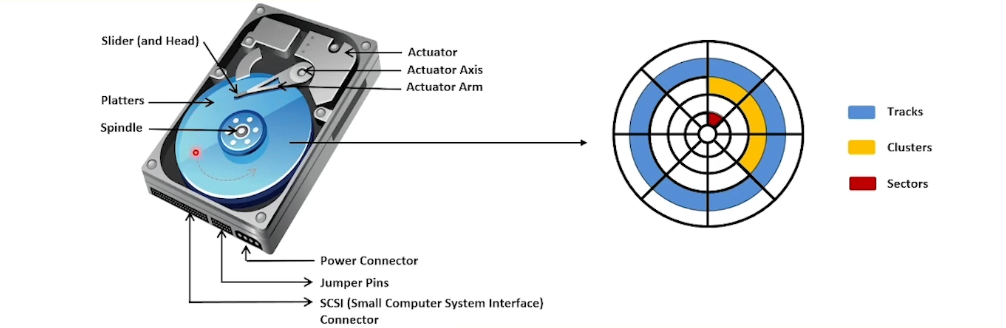
Understanding Hard Disk Drive:
Data is stored on the hard disk in the form of files.
Non-volatile digital data storage device.
Records data magnetically on a metallic platter. (ferrous oxide on top of plastic like material)
Read/Write performance of the HDD is directly proportional to the RPM of the drive platter.
Tracks:
Tracks are the concentric circles on platters where all the information is stored.
The drive head can access these circular rings in one position at a time.
Tracks are numbered for identification purposes.
Read/write is performed by rolling headers from the inner to outermost part of the disk.
Track Numbering:
Track number beings at 0.
Track location often referred to as cylinder number rather than track number.
A cylinder is a group of all tracks that start at the same head position on the disk.
Sector:
Smallest physical storage unit on a disk platter.
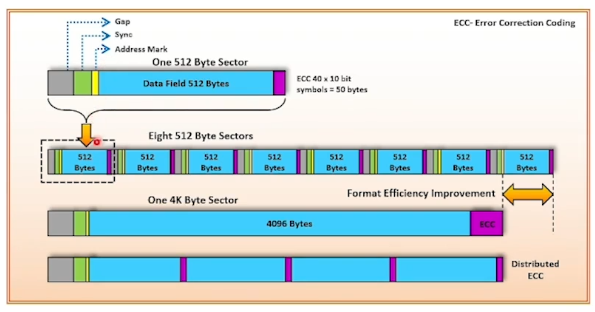
Each sector holds data of fixed size: 512 bytes for HDDs, 2048 bytes CD-ROMs & DVD-ROMs, latest HDDs use 4KB sectors.
Each disk sector is labelled using the factory track-positioning data.
The optimal method of storing a file on a disk is in a contiguous series.
Sector Addressing:
Cylinders, Heads, sectors (CHS) determine the address of the individual sectors on the disk.
When a disk is formatted, it is divided into tracks and sectors.
These are used by the OS and disk drive to identify the stored information.
4K sector is GENERATION-ONE ADVANCED format efficiently uses storage surface media by merging eight 512 bytes sectors into one 4k sector.
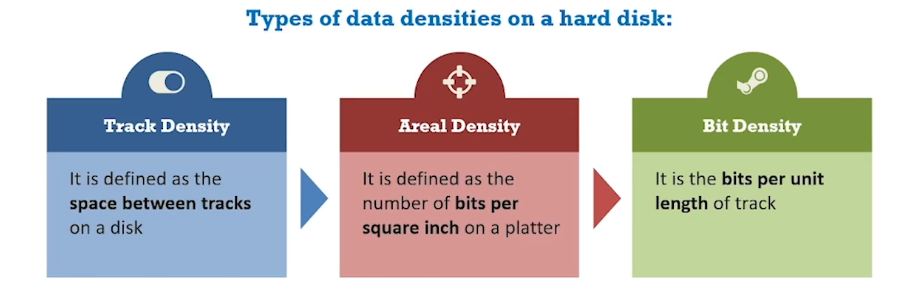
Data density on hard disk:
Zoned bit recording (or) multiple zone recording method is used to record data onto a hard disk.
Each zone is assigned a number of sectors per track.
In this method, tracks are combined together into zones depending on their distance from the center of the disk.
CHS data addressing: Cylinder-Head-Sector
The CHS addressing method addresses each physical block of data on a hard disk by specifying the cylinder (radius), head (platter side), and sector (angular position).
Total size of the disk = No. of cylinders * No. of Heads * No. of Sectors per track * No. of Bytes per sector.

Important
Hard Disk performance is measured by two factors: Data rate: Number of bytes per second that the hard disk sends to the CPU. Seek Time: Amount of time required to send the first byte of the file to the CPU, when it requests the file.
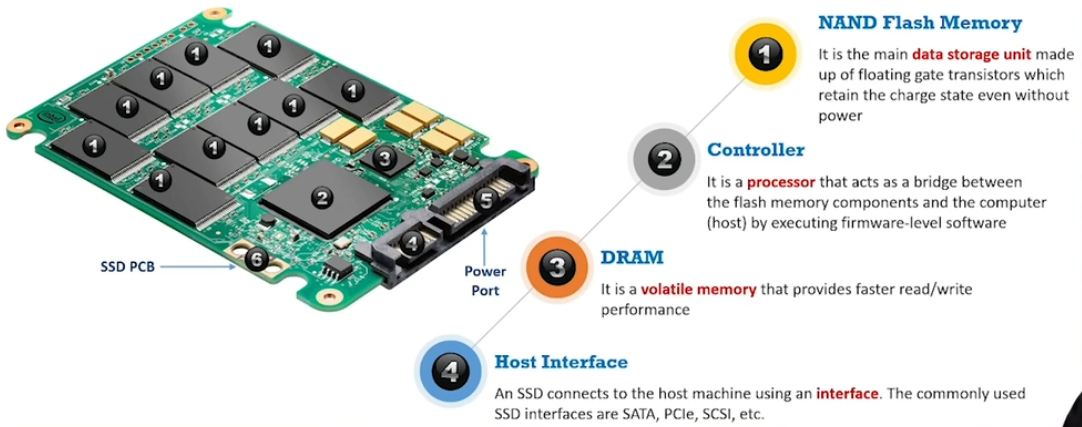
Understanding Solid State Drive:
Non-volatile storage device which uses NAND flash memory chips to store digital data
Read/Write performance depends on data connection of the drive.
Logical structure of Disks:
The logical structure of a hard disk is the file system and software utilized to control access to the storage on the disk.
Clusters:
It is the smallest logical storage unit on a hard disk.
In the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system, the clusters linked with a file keep track of file data in the hard disk’s file allocation table.
The file system divides the storage on a disk volume into discreet chunks of data for efficient disk usage and performance. These chunks are called clusters.
Cluster size can be altered for optimum disk storage.
Large cluster size → large unused area in cluster, small unused area in disk, min fragmentation problem.
Lost Clusters:
When the OS marks clusters as used but does not allocate them to any file, such clusters are known as lost clusters.
It mainly the result of a logical structure error and not a physical disk error.
It’s a FAT file system error.
It occurs because of interrupted file activities. Eg: a file is not properly closed.
CHKDSK is a system tool in Windows that authenticates the file system reliability of a volume and repairs logical file system errors
Slack Space:
Slack space is the storage space between the end of the file & the end of the cluster.
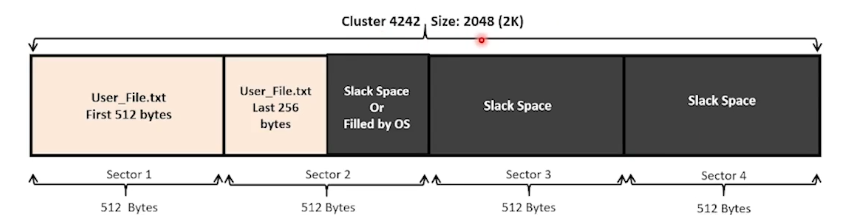
Slack space is not empty, it has some old data from the formatted disk
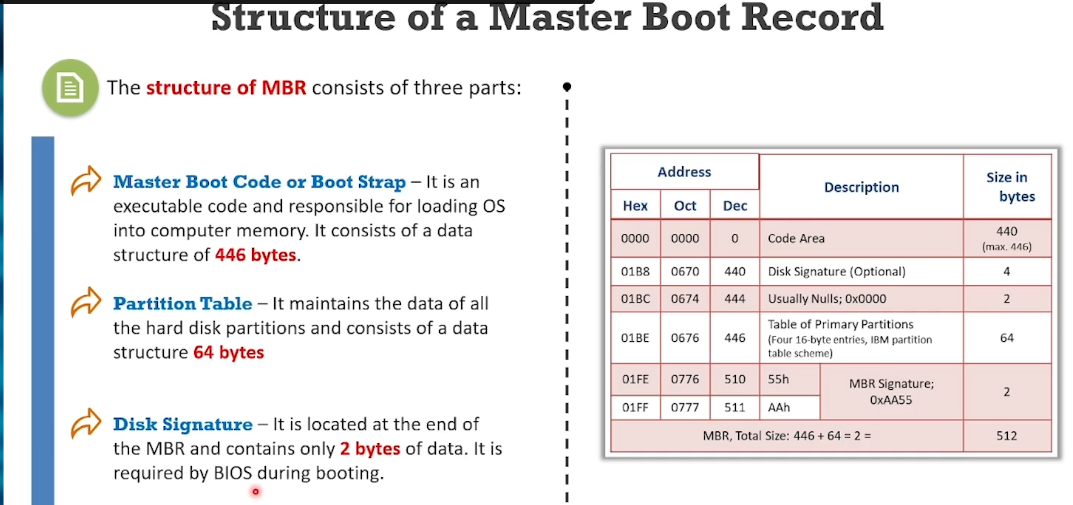
Master Boot Record:
MBR is the first sector of a data storage device such as a hard disk.
Info about files, locations, sizes are stored in MBR.
Holds the partition table.
Bootstrapping an OS.
Disk Partitioning process is same for both HDDs and SSDs.
Bios Parameter Block (BPB):
It is a data structure in the partition boot sector.
It describes the physical layout of a storage volume, Eg: no. of heads, size of tracks
BPB length varies for (FAT16, FAT32, NTFS) different boot sectors.
BPB assists investigators to locate the file table on the hard drive.
Globally Unique Identifier (GUID):
It is a 128-bit unique reference number, used as an identifier in computer software
displayed as 32 hexadecimal digits with groups separated by hyphens.
Used to identify COM & DLLs in windows registry.
used as primary key values in database tables.
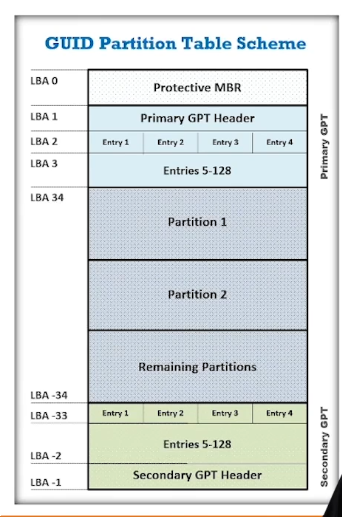
GPT (GUID Partition Table):
UEFI replaces legacy BIOS firmware interface. It uses partition system known as GUID Partition Table instead of MBR.
Supports up to 128 partitions uses 64 bit Logical block Addresses.
Max partition size from 2TiB to 8ZiB.
Provides primary and backup partition tables of redundancy.
Types of booting:
- Cold Boot or Hard boot - from the start
- Warm Boot or Soft boot - restart
Get-GPT -Path \.\PHYSICALDRIVE1

GPT Artifacts:

Mac Boot Process:
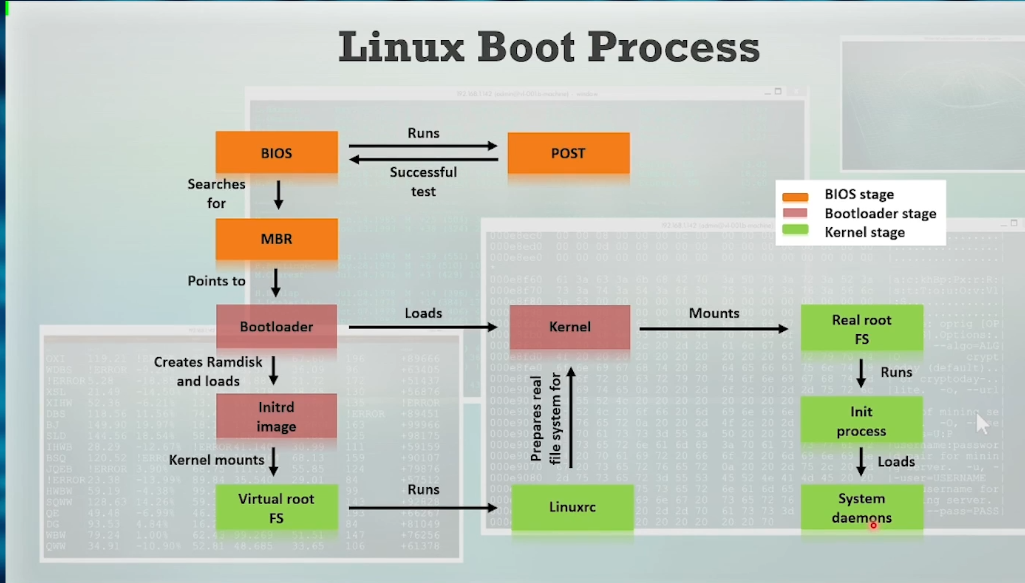
Linux Boot Process:
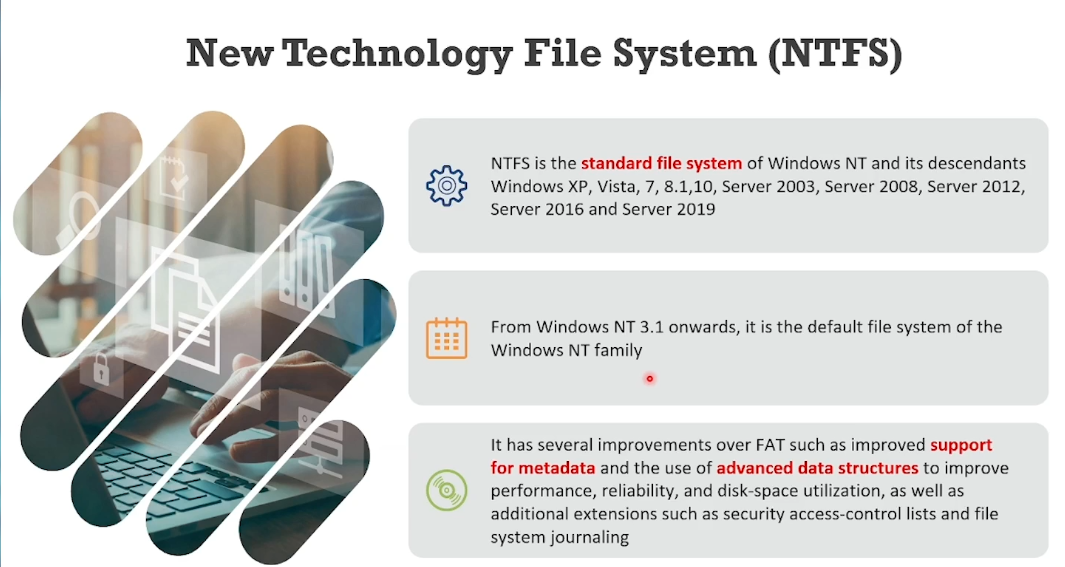
File systems of Windows:
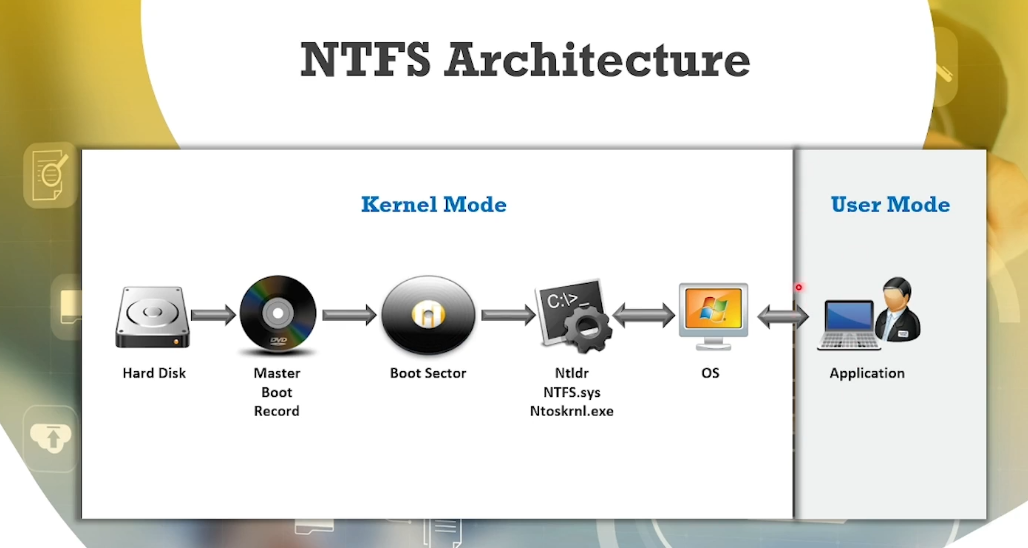
NTFS Architecture:
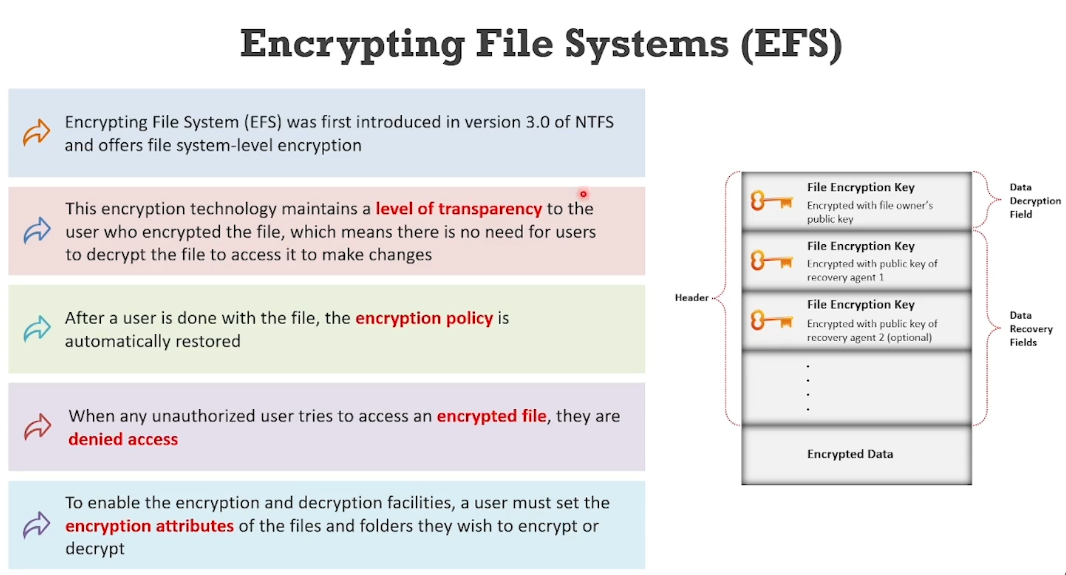
EFS:
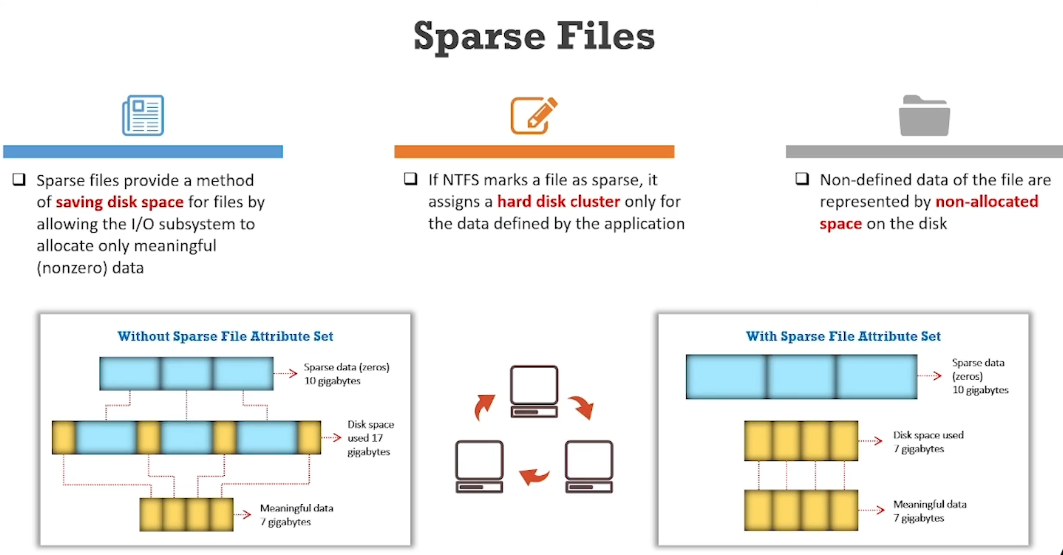
Sparse Files:
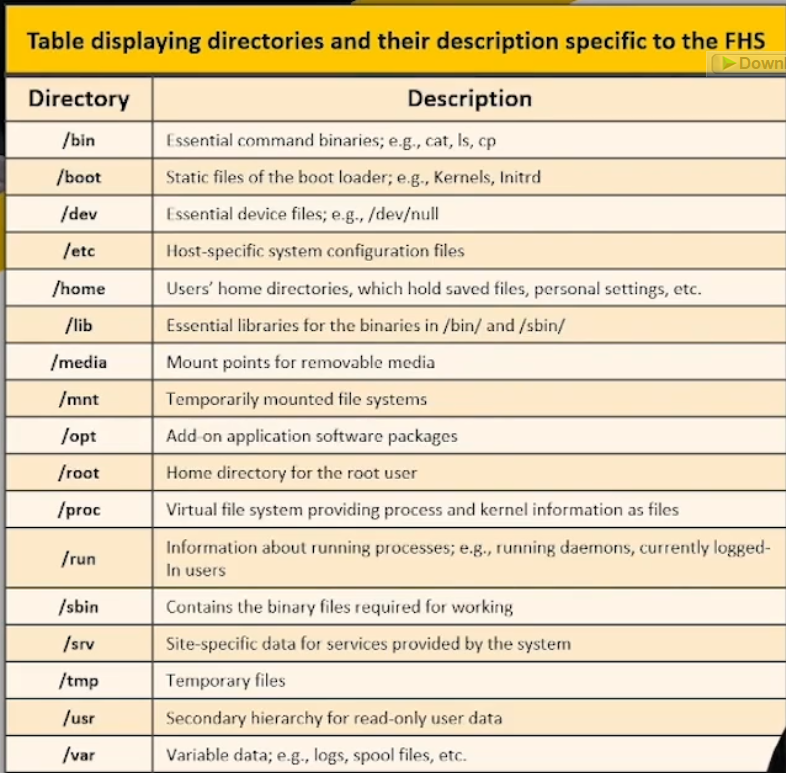
Linux File System:
Linus uses Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) that defines the directory structure and its contents in Linux and UNIX-like OSes.
In FHS, all files and directories are present under the root directory.
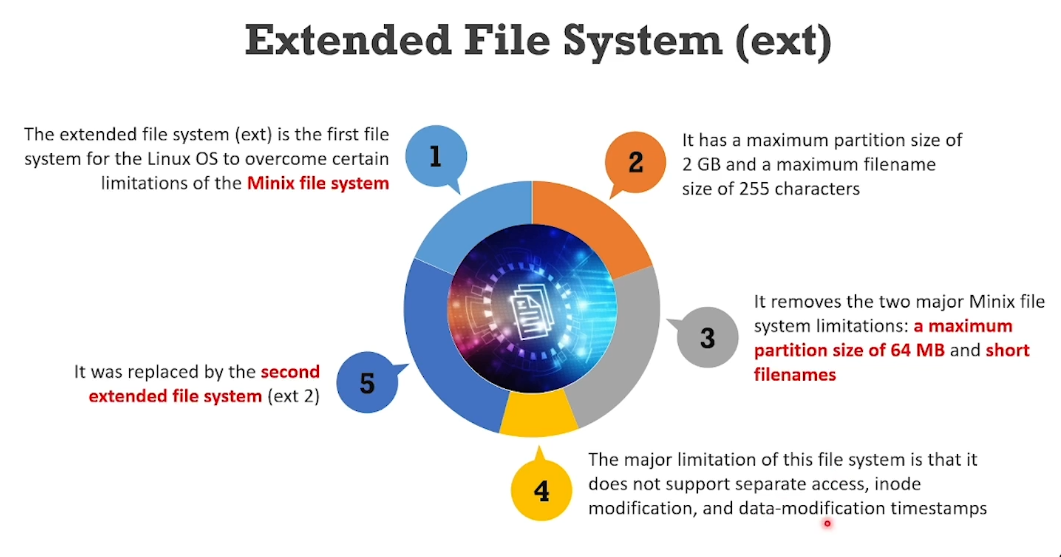
EXT:
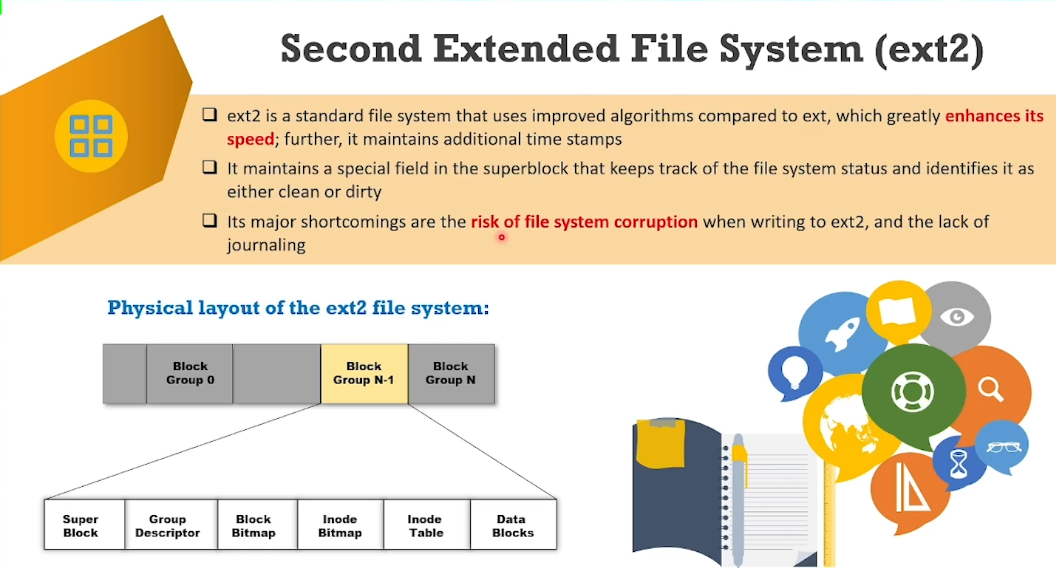
EXT2:
EXT3:
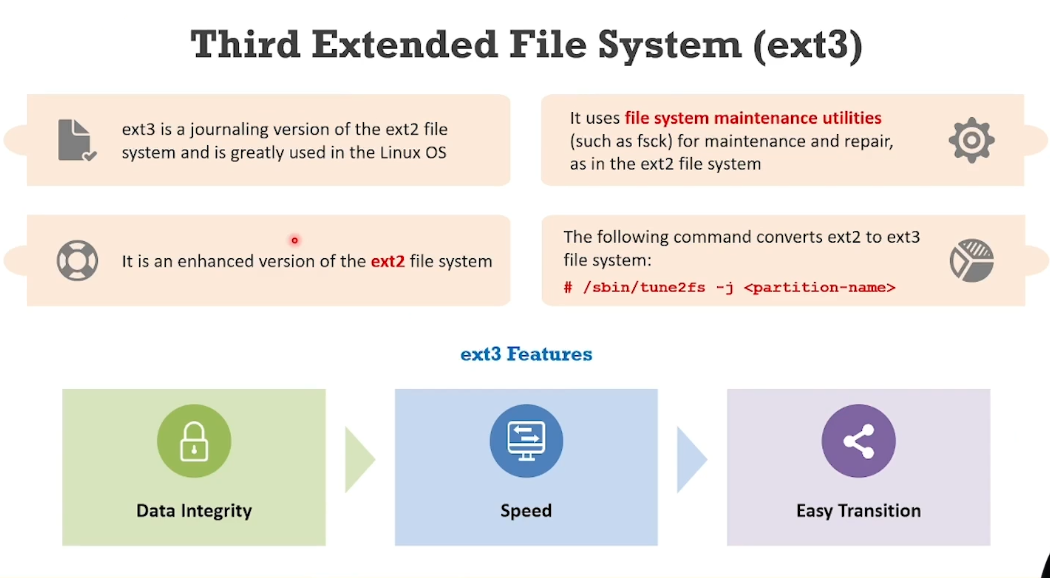
Journaling file system:
Journaling file systems ensure data integrity on a computer.
These file systems consist of a journal that
records all the information on the updates that are ready to be applied to the file system before they are applied. This mechanism is referred to as journaling.
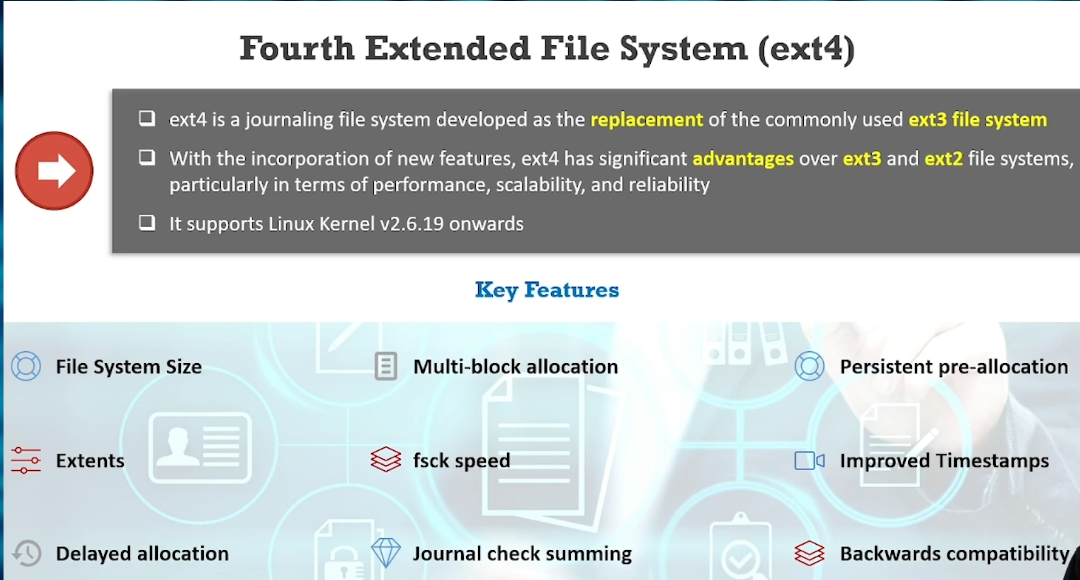
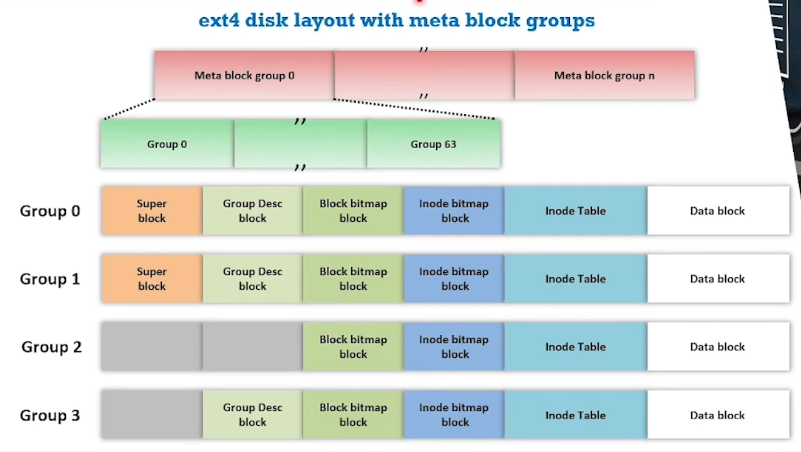
EXT4:
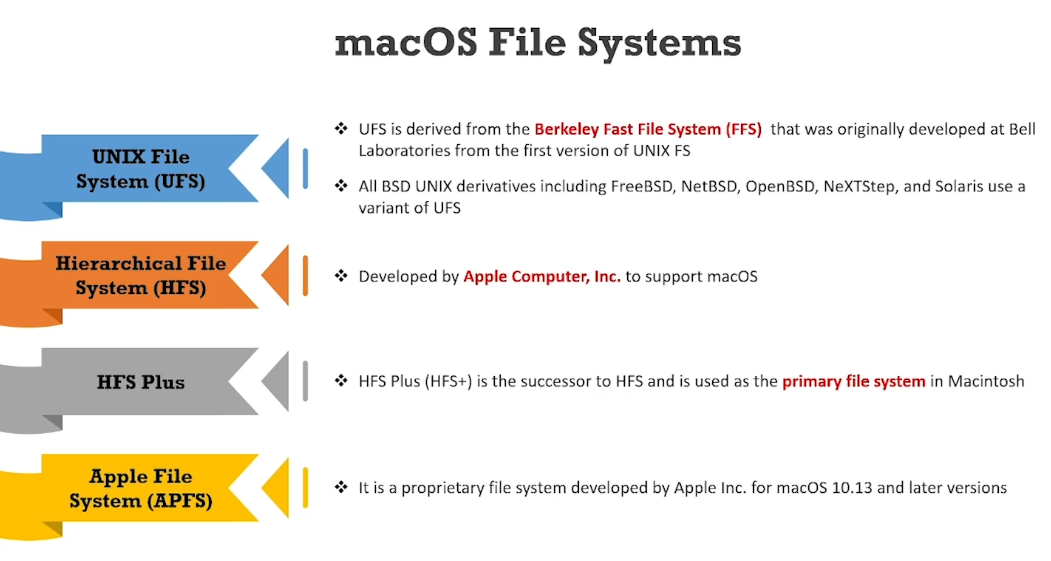
Mac File systems:
File System Analysis using Autopsy:
It can be used to investigate activities on a computer.

WinHex:
- WinHex is a hexadecimal editor, used for computer forensics, data recovery, low-level data processing, and IT security.
- It is mainly used to inspect and edit all types of files and to recover deleted files or lost data from hard drives with corrupt filesystems or from memory cards of digital cameras.