Cybersecurity 101: Specializations & Job Roles — Part I
A Little About Me:
I am a final year engineering student and a Cyber Threat Intel Analyst Intern in a cybersecurity company. I have worked in this intern position for the past one and a half years (22 months). I wanted to share stuff that would have been useful to me when I first started cybersecurity. This series will be helpful to all beginners who want to start a career in cybersecurity and to people who want to know what cybersecurity is all about.
Cybersecurity & its Specializations:
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from cyberattacks. Cybersecurity as a common word will include all the topics like hacking, defending, forensics, etc. As a member of this cybersecurity community, you should have a clear idea of what you should become in this vast area of cybersecurity. To know and try everything, I have categorized all the specializations that may be included in cybersecurity. By reading this, You will understand the opportunities you have in this industry and what job role will suit you.
Categories in Cybersecurity:
Cybersecurity is a broad field, and for beginners, it can be divided into several key categories:
- Offensive Security (Attack)
Offensive Security is about Ethical hacking. This is where we hack into systems, networks, software, etc., to find vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. This is the initial starting point for all the beginners in cybersecurity. If you are new to this field, start by trying offensive security to elevate your career to other categories. You should learn the technical part of this computer and internet world to be a master in this. But It is very much recommended to start your cybersecurity journey as a technical person. If you see all the big brains of cybersecurity today, you will find that most of them are from “System Administrator” background. This is where these people get hands-on experience in systems, networks, and servers. By this, they learn a lot about the technical aspects of the system.
Example Job Roles:
- Penetration Tester
- Red Team Specialist
- Bug Bounty Hunter
Where to Start:
Networking, Linux, Ethical hacking tools.
Platforms:
- TryHackMe — The best Beginner friendly platform
- OverTheWire — Best Platform to learn Linux (beginners start here)
- Cisco Networking Essentials Course — Beginner Networking Course
- NetworkAcademy.io — Networking for Beginners
- HackTheBox — Slightly Intermediate Challenges
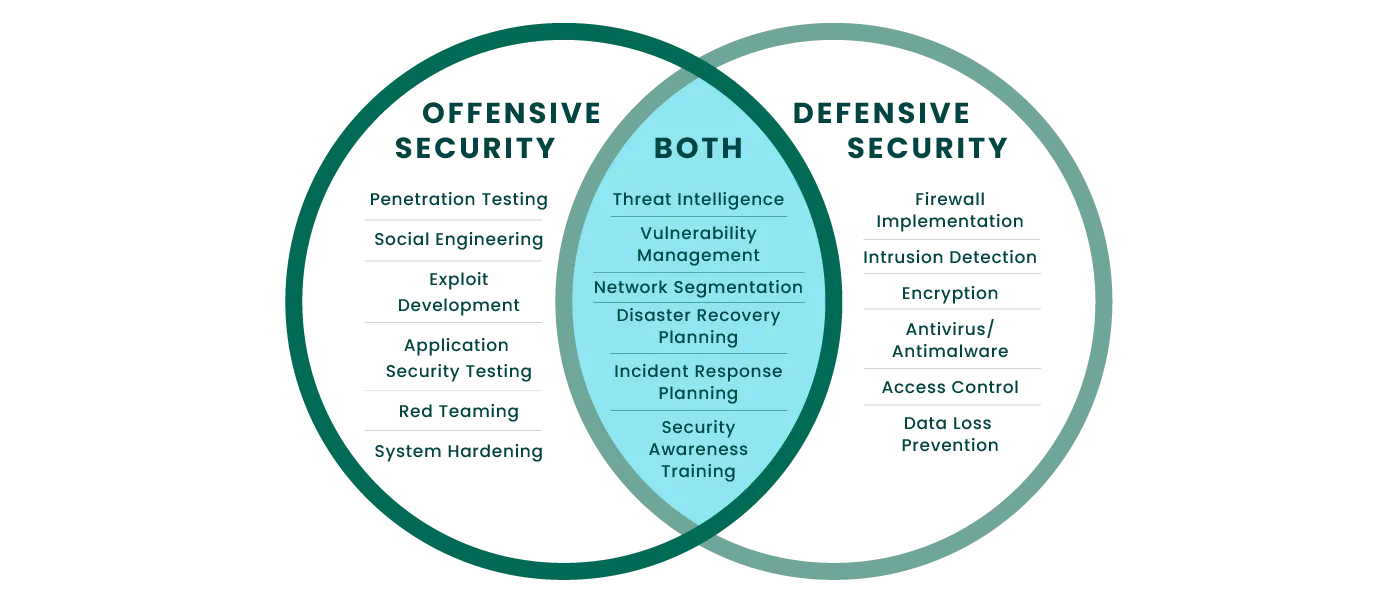
- Defensive Security (Defense)
Defensive Security focuses on protecting systems from cyber threats by implementing various security measures. This is another broad area, you can explore many things on the defensive side of cybersecurity. In this various types of work will include — hunting, monitoring, responding, and securing the systems, networks, and data. For everything, there is a job role in the market. You can research more on the below job roles to understand what people do in defensive security to secure the internet.
Example Job Roles:
- Security Analyst
- SOC Analyst
- Blue Team Specialist
- Threat Hunting
Where to Start:
First You should learn offensive security to focus on defense. You should know what an attacker might think to counter it and secure your system. You can start by learning about Threat hunting, and SOC tools. TryHackMe has a dedicated roadmap for this:
[TryHackMe | Cyber Security Training
TryHackMe is a free online platform for learning cyber security, using hands-on exercises and labs, all through your…
tryhackme.com](https://tryhackme.com/r/path/outline/soclevel1?source=post_page-----285f9bc1caca--------------------------------)
Also, Check out my notes for that SOC Level 1 learning path in Git Hub.
[GitHub - misterxcrypt/TryHackMe-Obsidian: This obisidian notes Contain Notes for SOC level 1 of Try…
This obisidian notes Contain Notes for SOC level 1 of Try Hack Me…! - misterxcrypt/TryHackMe-Obsidian
github.com](https://github.com/misterxcrypt/TryHackMe-Obsidian?source=post_page-----285f9bc1caca--------------------------------)
Platforms:
- Security Blue Team — Best Courses for the Defensive Side of Cybersecurity
- TryHackMe — Best Platform for Beginners
- Threat Intelligence
Threat Intelligence is an interesting category in Cybersecurity. To be honest, I didn’t know about Threat Intelligence until I joined this company. Nobody told me about threat intelligence and its importance in the cyber world when I first started in Cybersecurity.
Threat Intelligence involves gathering and analyzing data to predict and prevent attacks. The goal is to gather data about potential and existing threats to help organizations make informed decisions on how to defend against cyberattacks. It is about knowing the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) that attackers use, their motivations, and their targets. To be sophisticated in this category, you need to be updated in cyberspace, and constantly monitor different types of threats and threat actors relevant to your organization. Dark web monitoring and Telegram monitoring are key aspects of Threat Intelligence.
Example Job Roles:
- Threat Intelligence Analyst
- Vulnerability Analyst
- Cyber Threat Researcher
Where to Start:
Start by learning about different types of cyber threats that exist. Learn OSINT tools such as Maltego, Shodan, Fofa. Analytical thinking, knowledge of scripting languages (Python is very useful), and data analysis skills are crucial for threat intelligence.
Platforms: SANS Institute
- Research
Research in Cybersecurity helps advance the understanding of cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Researchers dig deep into the technical details of how attacks are carried out and develop methods to prevent or mitigate them. They focus on discovering new malware, and attack patterns, and understanding cybercriminal tactics. Of course, this category is not for beginners, but everyone should know what cybersecurity researchers do and what job roles are available in the market.
Example Job Roles:
- Malware Analyst
- Cryptographer
- Cybersecurity Researcher
Where to Start:
This category expects a good foundation in programming skills like C, C++, Python, and Assembly. These are essential for malware analysis, cryptography, etc. You should also be sophisticated in understanding, finding, mitigating, and replicating vulnerabilities. You can also look out for malware bazaar, and virus total to start your research journey.
Platforms:
It doesn’t have specific platforms to mention. You can check out below platforms for courses below:
- Cybrary
- SANS Institute
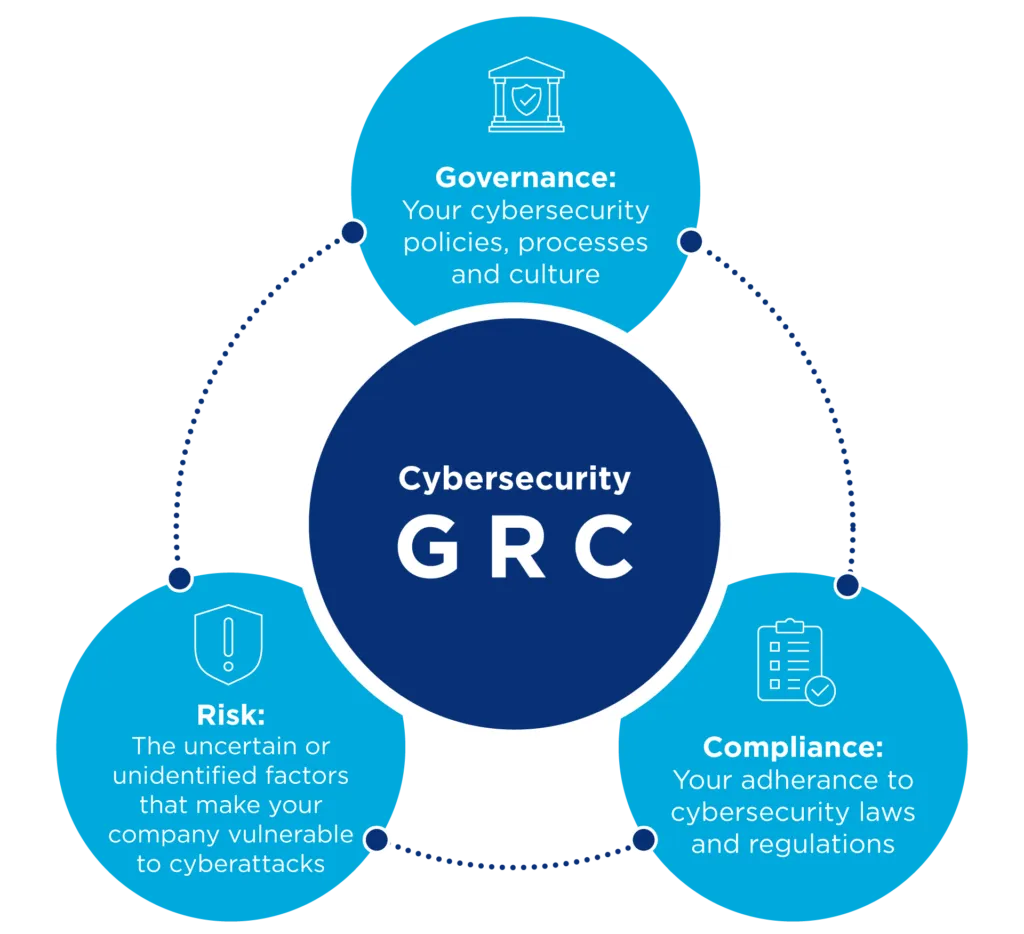
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance
GRC is a strategic approach in cybersecurity that focuses on aligning an organization’s IT practice with its business goals, managing risks, etc. It creates a secure and regulated environment in the organization while minimizing risks that could lead to data breaches, financial loss, etc. It is also a high-level job profile in cybersecurity, and not for beginners. It consists of people with little to no technical knowledge.
Example Job Roles:
- GRC Analyst
- Compliance Manager
- Security Auditor
Where to Start:
Learn the Basics of Cybersecurity regulations, standards, and frameworks. Learn about key compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. Focus on understanding risk assessment methodologies and learn how to create risk mitigation strategies.
Platforms:
- ISACA
- Cybrary
- CC in ISC2
- SANS Institute
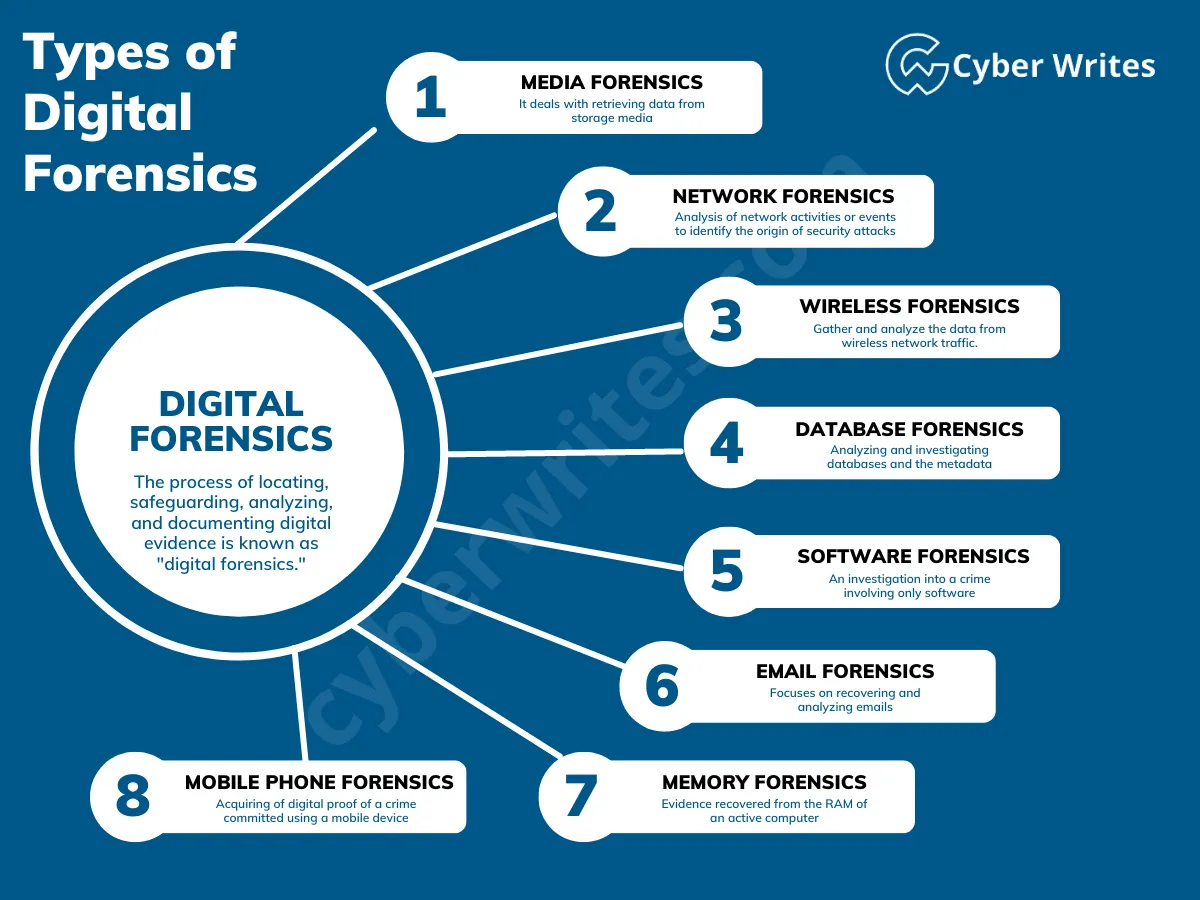
- Digital Forensics
Digital Forensics is an interesting field that helps in solving crimes involving digital stuff like laptops, computers, hard disks, pen drives, mobile phones, etc. Digital Forensics people investigate cyber incidents and recover data for analysis and also trace malicious activity. This knowledge can help you land government police jobs and also private jobs to analyze cyber-attacks. There are many kinds of forensics jobs available, I will put a blog on this topic specifically.
Example Job Roles:
- Forensics Expert
- Incident Responder
- Malware Analyst
Where to Start:
Learn the cybersecurity and networking fundamentals. Learn to use forensics tools like FTK, Encase, Autopsy, and Wireshark. You can also practice in Capture the Flag events.
Platforms:
- SANS Institute
- Magnet Forensics Academy
- Autopsy Training
- EC Council — Digital Forensics Essentials
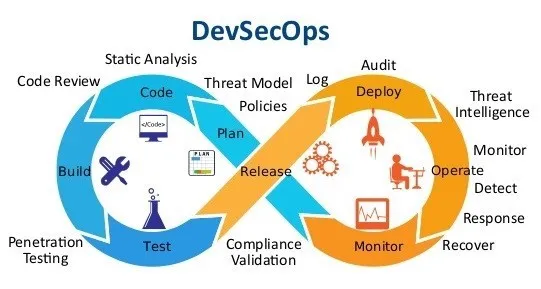
- Product Security
Product security focuses on securing software and hardware products during development and beyond. They only focus on securing their organization’s product. It involves integrating security practices into the product development lifecycle (SDLC), ensuring that vulnerabilities are identified and mitigated.
Example Job Roles:
- Product Security Engineer
- DevSecOps Engineer
- Cybersecurity Software Engineer
Where to Start: Learn secure coding practices, Understand DevSecOps Principles like CI/CD pipeline security, and Study security frameworks like OWASP.
Platforms:
- OWASP
- Docker Security
- Practical DevSecOps
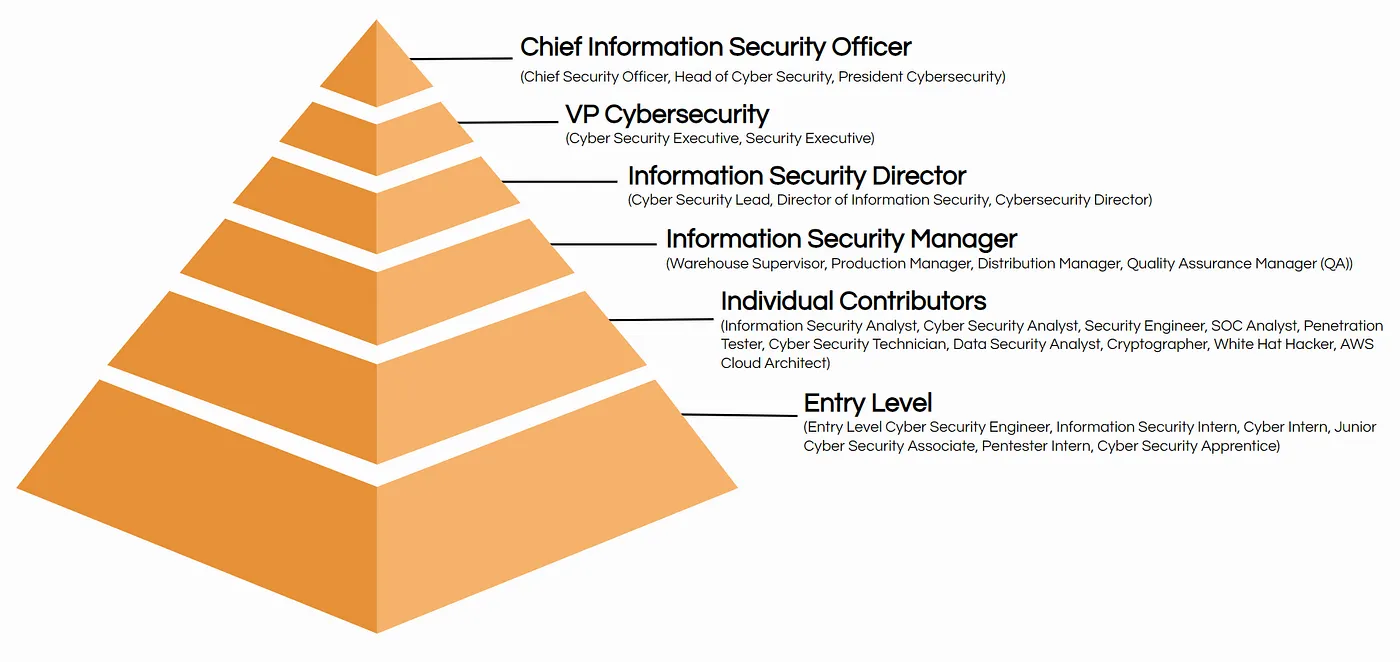
- Management
Management in Cybersecurity is about overseeing, guiding, and implementing strategies to improve the security of an organization. Cybersecurity managers mostly focus on ensuring that security policies and practices are up to date, covering every aspect of cyber threats to that organization to minimize risks of loss. Their decisions should always align with the goals of the organization.
Example Job Roles:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
- Chief Security Officer (CSO)
- Cybersecurity Lead
Where to Start:
Except for all the necessary fundamentals of cybersecurity and its nuances, You need to have great leadership skills. You should learn about cybersecurity regulations just like GRC people also you should have the ability to manage risks.
Platforms:
For these types of jobs, Experience talks more than your technical knowledge.
- SANS Institute
- ISACA
- Planning
Planning in cybersecurity involves designing, strategizing, and managing large-scale security projects. People like security architects, advisors, and consultants come under this category. This category needs a very high level of knowledge in cybersecurity. This category is focused on creating frameworks that guide the organization’s security posture to protect sensitive information and assets from potential threats.
Example Job Roles:
- Cybersecurity Project Manager
- Security Architect
- Cybersecurity Advisor
Where to Start:
Learning Project Management techniques and principles will help a lot in this category. Also, you should learn the security architect frameworks.
Platforms:
- Coursera & Udemy
- (ISC)2 — Certifications like CISSP
- SANS Institute
Where to Start in Cybersecurity?
- Learn the Basics: Study networking, system administration, and Linux.
- Pick a Category: Choose a category that excites you, whether it’s ethical hacking, defense, forensics, or management.
- Certifications: Entry-level certifications like EJPT or CEH are great starting points.
- Practice: Platforms like TryHackMe and Hack The Box allow real-world scenario practice. Also, Try out various Capture the Flag events to practice your learning.
- Stay Updated: Follow cybersecurity news, podcasts, and blogs to stay up to date on cyber threats, attacks, vulnerabilities, 0 days, etc.
Cybersecurity Specializations OffensiveSecurity DefensiveSecurity PenetrationTesting RedTeam BugBountyHunter SecurityAnalyst SOCAnalyst BlueTeam ThreatHunting ThreatIntelligence VulnerabilityAnalysis Maltego Shodan OSINT MalwareAnalysis Cryptography DigitalForensics IncidentResponse GRC GovernanceRiskCompliance ProductSecurity DevSecOps CISO SecurityManagement SecurityArchitect CyberThreats Certifications TryHackMe HackTheBox CaptureTheFlag CSO