OSINT
OSINT stands for open source intelligence and refers to the practice of collecting data from free sources that are available to the general public. As information becomes more available from a vast number of sources, skilled researchers can often find nearly any type of data they’re looking for, provided they know where to look. These sources include both public and private databases that hackers, journalists, spies, and ordinary people all use to do the work of collecting information every day.
Much of this information simply isn’t able to be retrieved through search engines and requires knowledge of where the right database is located to get the right answers. Fortunately, there are a multitude of tools that both beginners and seasoned investigators can take advantage of to use OSINT sources while conducting research.
OSINT Techniques
OSINT tactics can be divided into active and passive techniques, with active tactics involving some sort of actual contact with the target, and passive tactics avoiding any contact with the target. Active techniques always involve some small risk of the target detecting you are investigating them, whereas passive tactics usually involve querying a database maintained by someone else, and usually do not involve any risk of being detected.
An active OSINT tactic could be as simple as scanning a website or web server owned by a target, or registering to download a competitor’s product catalog. While this small contact probably won’t blow your investigation, matching a download to your organization’s IP address could tip off a subject that your organization is investigating. Comparatively, a passive technique like using a search engine like Shodan to examine services a company is running without scanning them yourself would be nearly impossible for the target to detect.

Concepts of OSINT
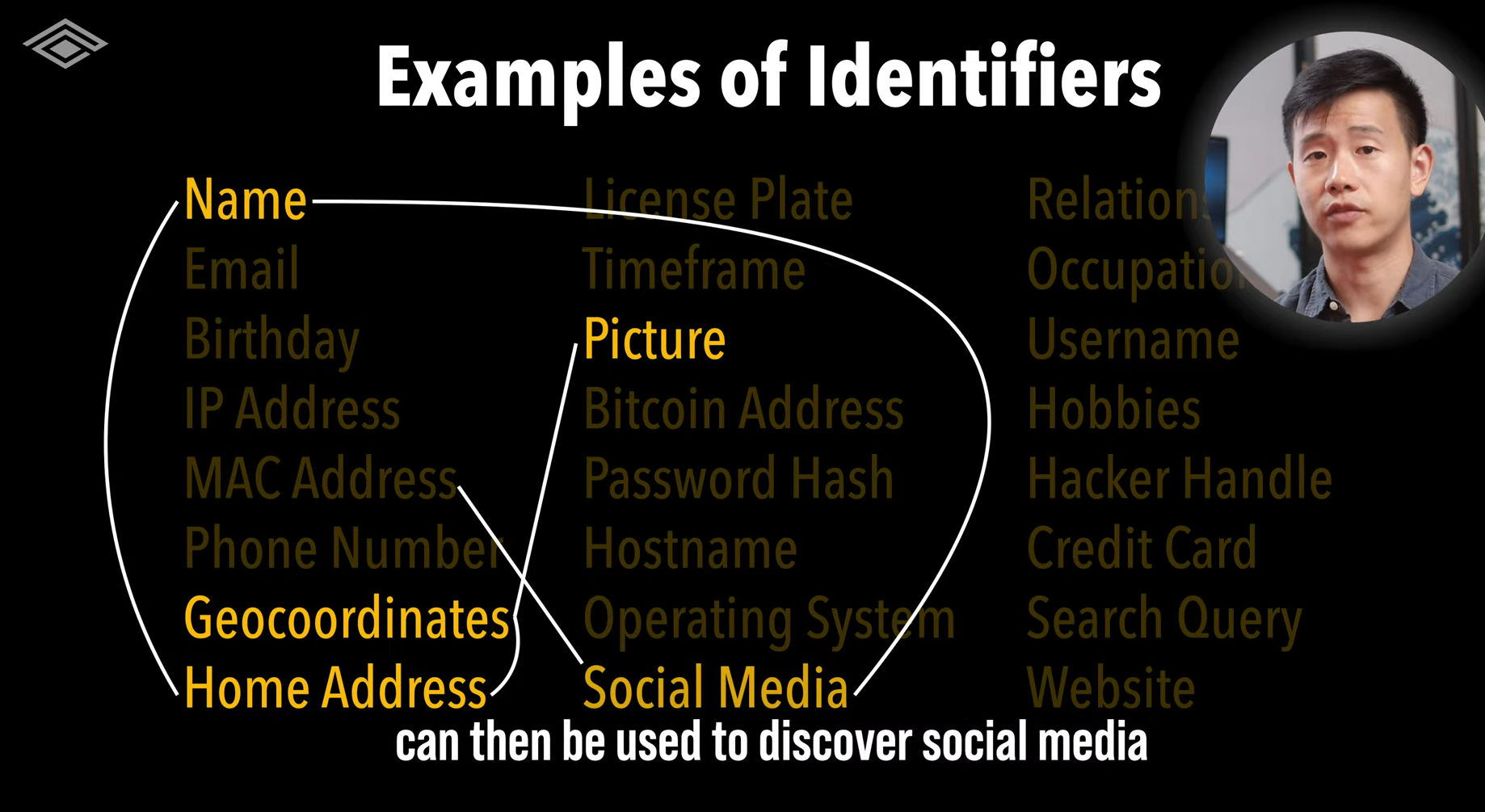
- Identifiers
- Pivoting

There are 4 stages of OSINT
Planning
Collection
Processing & Exploitation
Production
Dissemination & integration
1. Planning and Direction
The first step in the OSINT cycle involves planning the priorities
and requirements for the mission. Prior to collecting OSINT, operators
should have a clear understanding of the types of information they need,
how to find those sources, and what they hope to accomplish with the
acquired information. These precautionary logistics will guarantee the
productivity and efficiency of the operation during the next phases of
the OSINT cycle.
2. Collection
After proper planning has occurred, the collection of OSINT can
begin. OSINT resources include any materials that are freely available
online, such as news articles, social media posts, and blogs. Teams can
utilize their preferred collection tools and resources to obtain this
data.
3. Processing and Exploitation
Once you’ve acquired your data, you can start processing the
information. Then, you’ll want to compile it into a common evidence
repository, timeline, or report. In this stage, you’re simplifying the
content you’ve found and making it legible for the recipients of the
data. Processing the data will help analysts utilize the information
more efficiently in the following steps of the OSINT cycle.
4. Analysis and Production
After the initial processing of the collected data, your teams will
then need to perform an in-depth analysis of the information. This is a
crucial step in the OSINT cycle. as it will allow your teams to use the
data they’ve acquired to interpret and anticipate events. Operators can
organize their analyzed information into a detailed document or
presentation, which will be read by a designated audience.
5. Dissemination and Integration
The final step in the OSINT cycle entails delivering the collected
and analyzed intelligence to the proper stakeholders. Analysts then
receive feedback, which dictates whether the OSINT cycle should begin
again.