SNORT
Snort is the foremost Open Source Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) in the world. Snort IPS uses a series of rules that help define malicious network activity and uses those rules to find packets that match against them and generate alerts for users.
Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (NIDS/NIPS)
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
IDS is a passive monitoring solution for detecting possible malicious activities/patterns, abnormal incidents, and policy violations. It is responsible for generating alerts for each suspicious event.
There are two main types of IDS systems;
- Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) - NIDS monitors the traffic flow from various areas of the network. The aim is to investigate the traffic on the entire subnet. If a signature is identified, an alert is created.
- Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - HIDS monitors the traffic flow from a single endpoint device. The aim is to investigate the traffic on a particular device. If a signature is identified, an alert is created.
graph LR A[Intrusion Detection System] A--->B[Network IDS] A--->C[Host-based IDS]
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
IPS is an active protecting solution for preventing possible malicious activities/patterns, abnormal incidents, and policy violations. It is responsible for stopping/preventing/terminating the suspicious event as soon as the detection is performed.
There are four main types of IPS systems;
- Network Intrusion Prevention System (NIPS) - NIPS monitors the traffic flow from various areas of the network. The aim is to protect the traffic on the entire subnet. If a signature is identified, the connection is terminated.
- Behaviour-based Intrusion Prevention System (Network Behaviour Analysis - NBA) - Behaviour-based systems monitor the traffic flow from various areas of the network. The aim is to protect the traffic on the entire subnet. If a signature is identified, the connection is terminated.
Note note
The difference between NIPS and Behaviour-based is; behaviour based systems require a training period (also known as “baselining”) to learn the normal traffic and differentiate the malicious traffic and threats. This model provides more efficient results against new threats.
In case of any security breach during the training period, the results will be highly problematic.
- Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) - WIPS monitors the traffic flow from of wireless network. The aim is to protect the wireless traffic and stop possible attacks launched from there. If a signature is identified, the connection is terminated.
- Host-based Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS) - HIPS actively protects the traffic flow from a single endpoint device. The aim is to investigate the traffic on a particular device. If a signature is identified, the connection is terminated.
Detection/Prevention Techniques
There are three main detection and prevention techniques used in IDS and IPS solutions:
| Technique | Approach |
| Signature-Based | This technique relies on rules that identify the specific patterns of the known malicious behaviour. This model helps detect known threats. |
| Behaviour-Based | This technique identifies new threats with new patterns that pass through signatures. The model compares the known/normal with unknown/abnormal behaviours. This model helps detect previously unknown or new threats. |
| Policy-Based | This technique compares detected activities with system configuration and security policies. This model helps detect policy violations. |
Snort quote
“Snort can be deployed inline to stop these packets, as well. Snort has three primary uses: As a packet sniffer like tcpdump, as a packet logger — which is useful for network traffic debugging, or it can be used as a full-blown network intrusion prevention system. Snort can be downloaded and configured for personal and business use alike.”
Snort has three main use models:
- Sniffer Mode - Read IP packets and prompt them in the console application.
- Packet Logger Mode - Log all IP packets (inbound and outbound) that visit the network.
- NIDS (Network Intrusion Detection System) and NIPS (Network Intrusion Prevention System) Modes - Log/drop the packets that are deemed as malicious according to the user-defined rules.
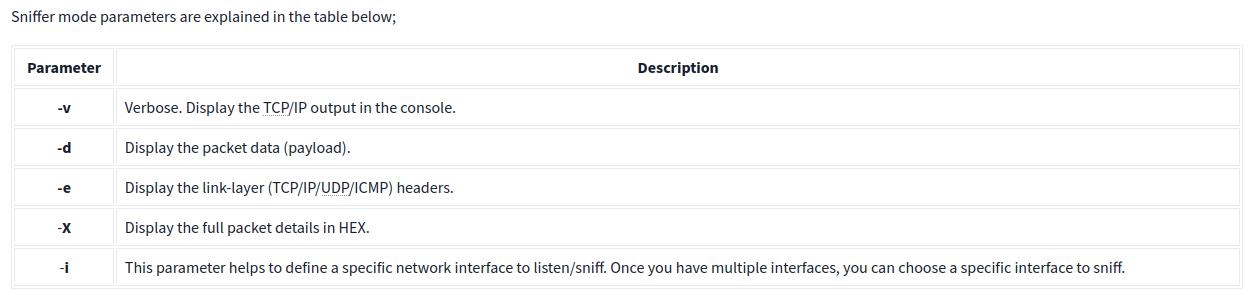
Sniffer Mode
Logger Mode

NIDS

PCAP Parameters

SNORT Rule Structure
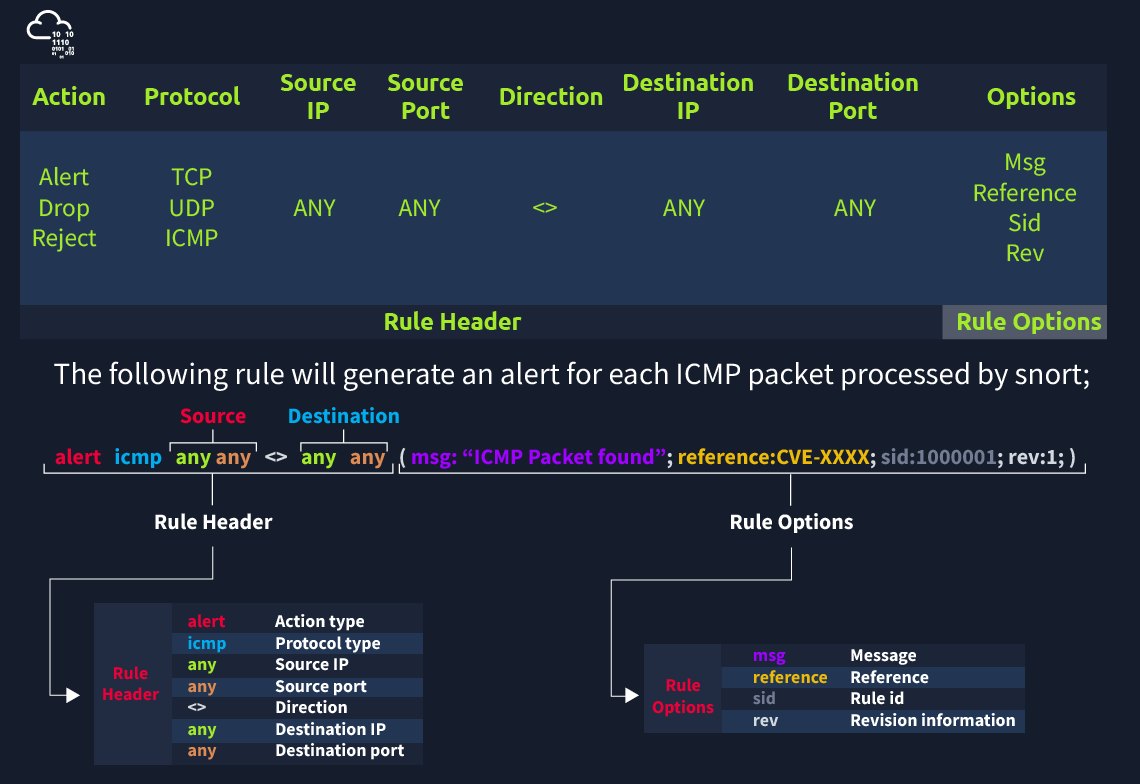
Two actions; “alert” for IDS mode and “reject” for IPS mode.
Action
- alert: Generate an alert and log the packet.
- log: Log the packet.
- drop: Block and log the packet.
- reject: Block the packet, log it and terminate the packet session.
Protocol
Snort2 supports only four protocols filters in the rules (IP, TCP, UDP and ICMP). However, you can detect the application flows using port numbers and options. For instance, if you want to detect FTP traffic, you cannot use the FTP keyword in the protocol field but filter the FTP traffic by investigating TCP traffic on port 21.
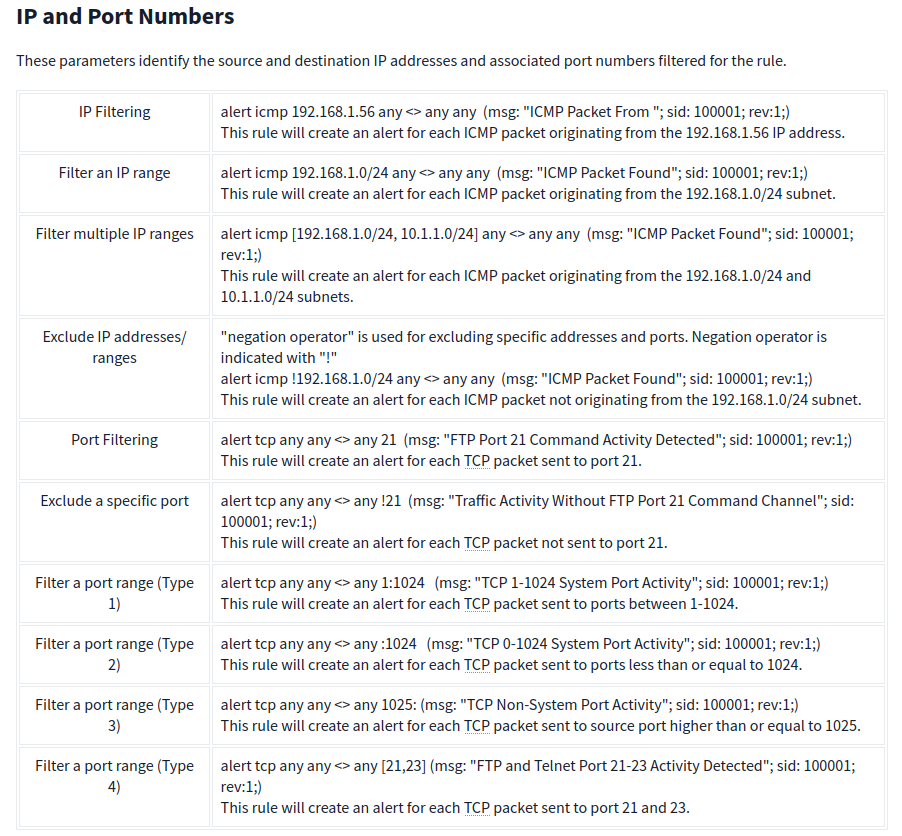
Direction
The direction operator indicates the traffic flow to be filtered by Snort. The left side of the rule shows the source, and the right side shows the destination.
- → Source to destination flow.
- <> Bidirectional flow
There are three main rule options in Snort;
- General Rule Options - Fundamental rule options for Snort.
- Payload Rule Options - Rule options that help to investigate the payload data. These options are helpful to detect specific payload patterns.
- Non-Payload Rule Options - Rule options that focus on non-payload data. These options will help create specific patterns and identify network issues.


